Course Information
Lean Manufacturing Training
Learners will be able to:
- Streamline the value stream using current and future state value stream mapping.
- Organize the workplace making it more efficient and reducing waste.
- Improve product and process predictability and consistency.
- Reduce set-up and equipment downtime.
- Develop a Lean implementation plan.
- Avoid common Lean implementation pitfalls.

About This Course
Simply put, lean organizations are customer-focused. They reduce waste in their value streams by improving workflows and then by subsequently improving the physical layout of their facilities. Process capacity is managed and actually increased by reducing set-up times, improving quality, and ensuring equipment works when it is counted upon to work.
Successful implementation of a lean initiative will improve an organization’s marketplace and financial performance. However, many aspects of lean are counter-intuitive to traditional manufacturing thinking and practices. It is vital that organizations adopting a lean approach understand the scope, the many elements, and the potential pitfalls of lean.
Lean Manufacturing Training provides learners with a comprehensive understanding of how Lean Manufacturing works in a manufacturing company. Lean concepts (why lean, lean terminology, identifying wastes, Value Stream Mapping methods and the linkage between lean and Six Sigma) and lean practices (streamlining the value stream, workplace organization, ensuring predictability and consistency, set-up reduction, TPM, the visual workplace and continuous improvement) are covered. Lean Manufacturing Training provides the learner with lean implementation suggestions including approaches for addressing people issues, collecting and analyzing data to plan and track lean efforts, process workflow and layouts options with rationale and a sequential roadmap.
- Understanding and application of the principles of the 5S’s such as Introduction to the 5S’s or equivalent.
- English (EN-US)
- Chinese (simplified) (ZH)
- Czech (CS)
- French (FR)
- German (DE)
- Italian (IT)
- Japanese (no audio) (JA)
- Korean (no audio) (KO)
- Polish (PL)
- Portuguese (Brazilian) (PT-BR)
- Romanian RO)
- Russian (RU)
- Spanish (ES)
- Vietnamese (no audio) (VI)
Course Objectives
Unit 1 | Lean Concepts
- Understand the reasons for implementing lean.
- Learn the terms, tools, and techniques used in lean.
- Identify the types of waste that can be eliminated with lean.
- Describe the components and elements of a lean effort.
- Explain value stream mapping, techniques for analyzing the current state map and for envisioning the future state of the workflow.
- Describe why and how lean can apply to finance, maintenance, sales and R&D processes.
- Compare and contract the linkages and differences between lean and six sigma initiatives.
Unit 2 | Lean Practices
- Streamlining the Value Stream: Learn how to use value stream maps to create macro-facility workflows and micro-process workflows.
- Workplace Organization: Understand how the 5S’s establish a structured approach for storing materials, supplies, and equipment in work areas.
- Predictability & Consistency: Discover how quality improvement techniques such as GR&Rs, SPC, DOE, DFA/DFM, and (especially) mistake-proofing help prevent problems and lead to robust processes.
- Set-Up Reduction: Investigate how to slash set-up and change-over times and understand how important fast set-ups are to lean efforts.
- TPM: Learn how to improve equipment reliability by applying TPM methods.
- Visual Workplace: See how visual controls and visual displays reinforce and enhances a lean effort.
- Support Processes: Recognize how important lean scheduling, lean purchasing, lean accounting, and lean warehousing practices are to supporting and sustaining a lean manufacturing effort.
- Continuous Improvement: Explore the options for keeping a lean effort viable and vital.
Unit 3 | Implementing Lean
- Understand how important it is to address people issues as cross-training and flexible staffing practices are introduced.
- Review the types and forms of data needed to support lean implementation.
- Explore forms used to help plan and track lean efforts.
- Investigate layout options and methods to determine the best option for your workflow and facility.
- Learn how a lean warehouse complements lean manufacturing.
- Review a systematic roadmap for introducing and implementing lean.
- Explore 12 common lean pitfalls and learn how to avoid them.
Course Outline
Unit 1 Lean Concepts
Lesson 1 | Why Lean?
- Be customer focused: Be on-time, responsive, flexible, and fast.
- Simplify and standardize workflows: Mimic continuous flow, minimize WIP, use visible measures.
- Manage capacity: Increase process uptime, reduce set-up times, find “lost” capacity.
- Eliminate waste: Identify non-value adding activities, then modify, combine, or eliminate those tasks.
- JiT: Not too early and never late; not just-in-case inventory but just-in-time production and delivery; products must always be made right the first time; equipment must always work when needed.
Lesson 2 | Lean Terminology
- Terms
- Tools
- Techniques
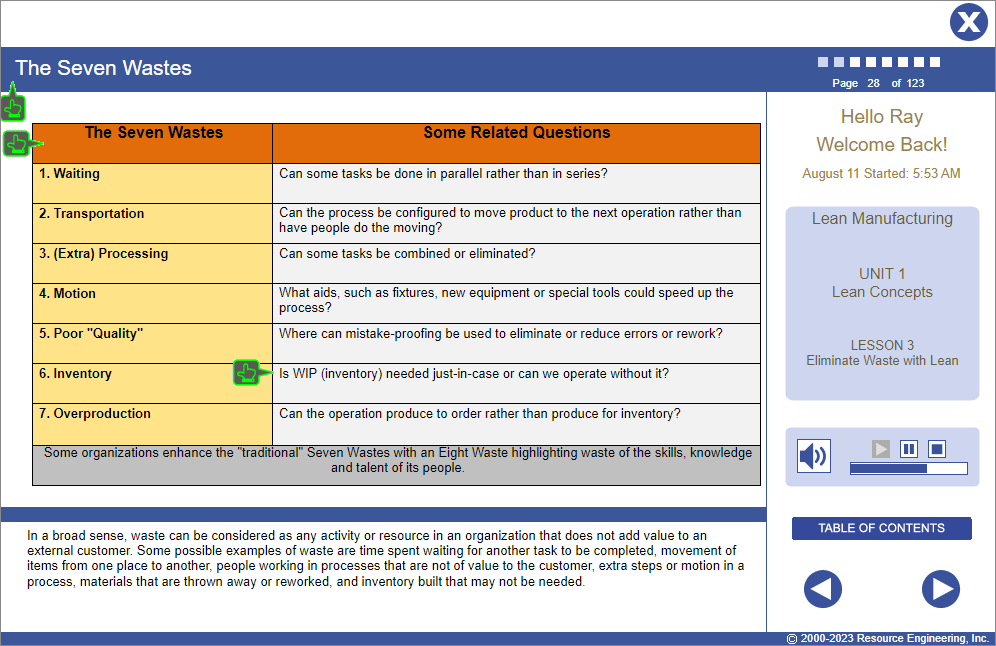
Lesson 3 | Eliminate Waste
- Match lot sizes to customer demands: Use kanbans; end WIP.
- Use pull scheduling instead of push scheduling.
- Schedule to the rate-determining step (the bottleneck), then de-bottleneck process lines.
- Facilitate fast feedback: Arrange sequential operations next to each other to ensure fast feedback from internal customer operations to internal supplier operations if something in-process is not right.
Lesson 4 | Components of Lean
- Overview of the 8 Components of Lean: Value Stream Mapping, Workplace Organization, Predictability and Consistency, Set-up Reduction, TPM, Visual Factory, Support Processes, and Continuous Improvement.
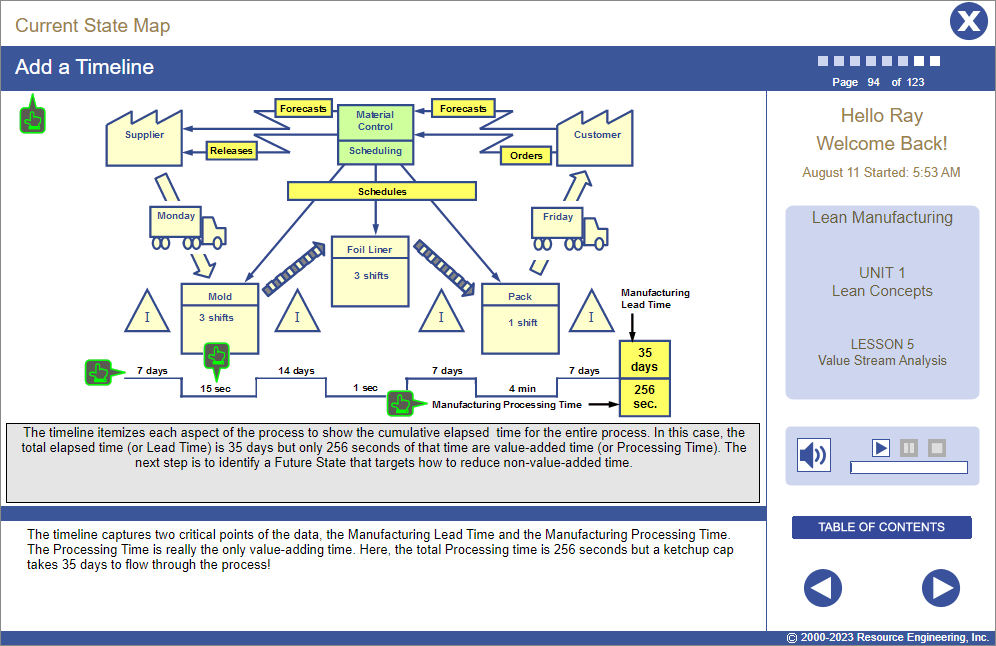
Lesson 5 | Value Stream Analysis
- Map the process from incoming order to outgoing product: Define process goals, create the current state map, and establish process metrics.
- Use the current state map to identify potential improvements, conceive the future state.
Lesson 6 | The Lean Mindset
- Eliminating waste is not limited to manufacturing; the same techniques apply to the office, sales, finance, maintenance, and even RandD processes and procedures.
- Lean and Six Sigma are complementary.
Unit 1 Challenge
- An assessment of the learner’s progress in this unit.
Unit 2 Lean Practices
Lesson 1 | Streamlining the Value Stream
- Identify process goals.
- Collect and analyze process data.
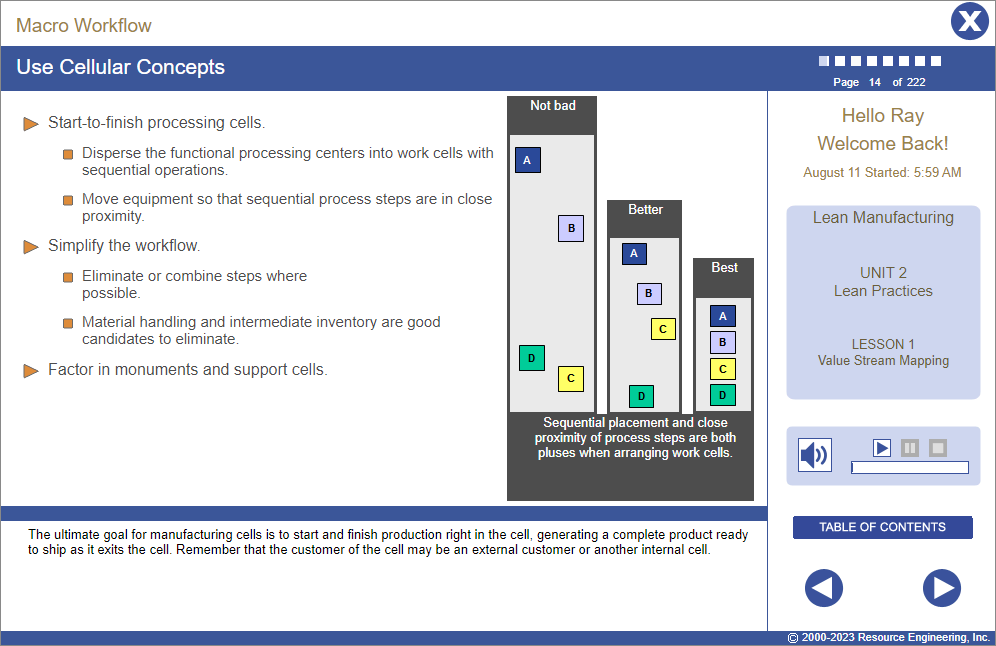
- Create a macro-facility workflow to determine how to minimize high volume travel distances.
- Conduct a micro-process workflow to apply cellular concepts, identify and remove bottlenecks, and move to pull manufacturing with kanbans.
Lesson 2 | Workplace Organization
- Apply the 5Ss: Sort (clearing the work area), Set in Order (designating locations), Shine (cleanliness and workplace appearance), Standardize (everyone doing things the same way), and Sustain (ingraining it in the culture).
Lesson 3 | Predictability and Consistency
- Use DFA/DFM to design quality in.
- Conduct GRandRs to ensure reliable measurement systems are in place.
- Employ SPC to help ensure processes are predictable and stable.
- Reduce variation and improve process capability with DOE.
- Eliminate the root cause of defects using problem-solving and mistake-proofing.
- Move to Six Sigma quality.
Lesson 4 | Set-Up Reduction
- Apply SMED concepts.
- Separate external tasks (external to the process) from internal tasks.
Lesson 5 | TPM
- TPM versus PM
- Develop operator involvement in the equipment and begin predictive maintenance practices.
Lesson 6 | Visual Workplace
- Visual Workplace
- Use status display of performance for dashboard or balanced measures and COQ results.
- Visual controls, such as sensory alerts, indicate if something is out of place.
- Marking on the floor, kanbans, andons, and panel-alarms all help build a visual control infrastructure.
Lesson 7 | Support Processes
- Lean techniques require changes in Purchasing, Scheduling, Warehousing/Shipping, and Accounting practices.
Lesson 8 | Continuous Improvement
- Fight NIH (not-invented-here) attitudes and leverage successes.
- Use kaizen events for rapid, targeted improvements to achieve the future state.
- Use a standardized Problem-Solving Model (e.g. DMAIC or 8D).
- Begin an employee idea system.
Unit 2 Challenge
- An assessment of the learner’s progress in this unit.
Unit 3 Implementing Lean
Lesson 1 | Lean Starts with People
- Lean Starts with People
- Communicate the why, what, how, and who.
- Provide education in the concepts.
- Train employees in tools and techniques as needed to achieve a flexible workforce.
Lesson 2 | Data Drives Lean
- Focus efforts on projects that lead to tangible savings.
- Calculation techniques to generate data include: Time studies, equipment loading, TAKT time, staffing requirements, process yields, and COQ.
- Sample Worksheets covered include: Lean Project Summary; Cell Target Worksheet; Data Collection Form for Basic Equipment and Utility Parameters; Value-Adding Analysis Worksheet; Process Change-Over/Setup Worksheet; Set-Up Reduction Worksheet; and Lot Size Worksheet.
Lesson 3 | Layout Options
- Improved layouts are about moving cubic feet (not numbers of items), eliminating crossover points, arranging the process in the natural flow order; linking processes to minimize time and distance; moving equipment together to simulate a continuous process flow; and putting internal customers and suppliers next to each other.
- Be careful to identify anchors or monuments; do not move them.
- Typical layout options are explored.
Lesson 4 | Lean Inventory Practices
- Minimize trips to and from the warehouse by designing the warehouse to work for you.
- Use ABC inventory categories to prioritize inventory needs and storage locations.
Lesson 5 | Roadmap for Lean
- Start with the people issues.
- Focus on workplace organization (the 5S’s), then, use value stream analysis and process workflow analysis to establish effective layouts.
- Where to focus next depends on specific needs.
- Use targeted Kaizen events to speed changes.
- Do not overlook the need to modify support processes (especially scheduling and purchasing).
Lesson 6 | Lean Pitfalls
- Not documenting the financial impact/savings.
- Lack of commitment from leadership.
- Using traditional purchasing practices.
- Not changing scheduling techniques.
- Failure to address workforce issues.
- Not mistake-proofing the root cause.
- Thinking Lean is just for manufacturing.
- Not using beneficial technology.
- Not leveraging successes.
- Getting too lean.
- Failure to hold the gains.
Unit 3 Challenge
- An assessment of the learner’s progress in this unit.

4.5 out of 5 stars
Comments from Learners About This Course
- I really enjoyed the course! It is complete enough for the perfect understanding of Lean methodology! Very good!
- Very informative course.
- Excellent!! Great content!
You may also be interested in…
- The 5S’s: Workplace Organization – Comprehensive training in the concepts and application of the 5S’s (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize and Sustain) and how to apply these techniques on the job.
- Lean for Job Shops – Online training in how to apply lean manufacturing techniques in short-run, job shop environments.
- Mistake-Proofing Training – Comprehensive online training in poka yoke/mistake-proofing techniques for manufacturing operations.