Course Information
Overview of Lean Training
Learners will be able to:
- Describe the key concepts of Lean.
- Explain how Lean practices can reduce non-value-added waste.
- Identify the major components of successful Lean initiatives.

About This Course
What is Lean Manufacturing?
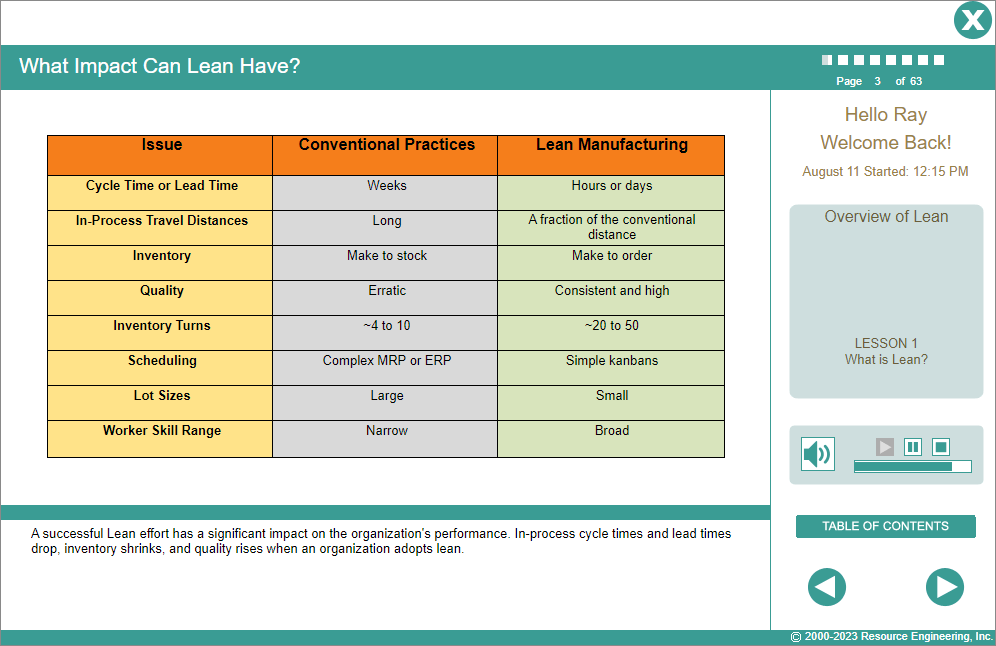
Simply put, lean organizations are customer-focused. They reduce waste in their value streams by improving workflows and then by subsequently improving the physical layout of their facilities. Process capacity is managed and actually increased by reducing set-up times, improving quality, and ensuring equipment works when it is counted upon to work.
Successful implementation of a lean initiative will improve an organization’s marketplace and financial performance. However, many aspects of lean are counter-intuitive to traditional manufacturing thinking and practices. It is vital that organizations adopting a lean approach understand the scope, the many elements, and the potential pitfalls of lean.
Overview of Lean Online Training
This course provides an overview of the principles and practices of Lean. It is a great starting point for organizations to introduce managers and employees to the concepts and benefits of Lean Manufacturing.
- None.
- English (EN-US)
- Chinese (simplified) (ZH)
- Czech (CS)
- French (FR)
- German (DE)
- Italian (IT)
- Japanese (no audio) (JA)
- Korean (no audio) (KO)
- Polish (PL)
- Portuguese (Brazilian) (PT-BR)
- Romanian RO)
- Russian (RU)
- Spanish (ES)
- Vietnamese (no audio) (VI)
Course Objectives
- Describe the key concepts of lean manufacturing.
- Name and describe the seven wastes.
- Briefly describe how each of the seven wastes add costs to a process.
- Define value-adding and non-value adding.
- List the eight components of lean and define each.
Course Outline
Lesson 1 | Why Lean?
- Be customer focused: Be on-time, responsive, flexible, and fast.
- Simplify and standardize workflows: Mimic continuous flow, minimize WIP, use visible measures.
- Manage capacity: Increase process uptime, reduce set-up times, find “lost” capacity.
- Eliminate waste: Identify non-value adding activities, then modify, combine, or eliminate those tasks.
- JiT: Not too early and never late; not just-in-case inventory but just-in-time production and delivery; products must always be made right the first time; equipment must always work when needed.
Lesson 2 | Eliminate Waste
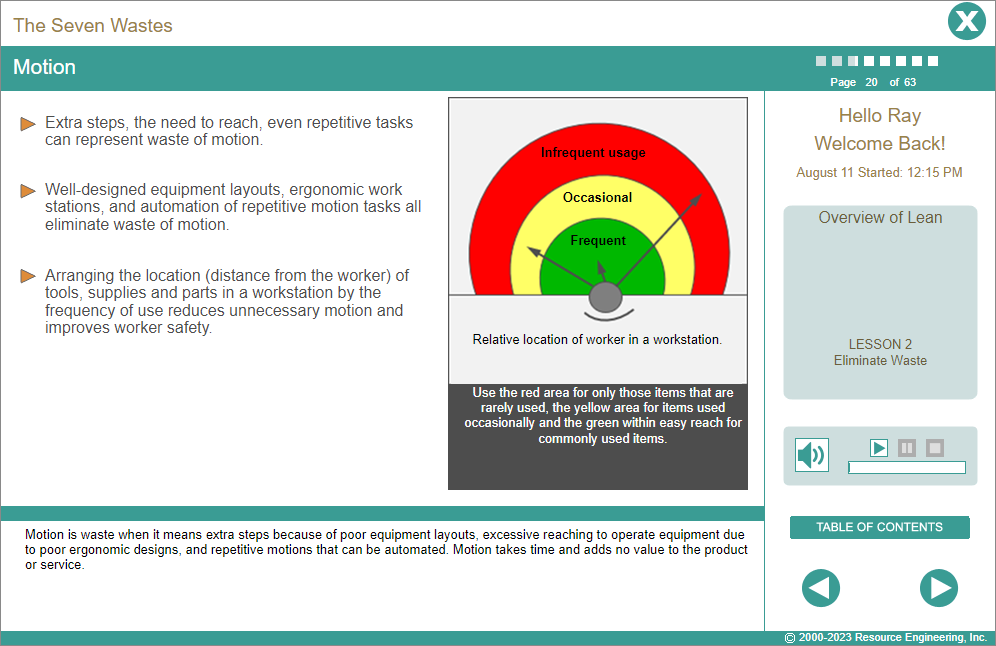
- Elimination of waste starts with identification of waste. Anything that does not add value is classified as waste.
- Waste can be classified into seven categories: Waiting, Transportation, Processing, Motion, Quality, Inventory and Overproduction.
Lesson 3 | Components of Lean
- Overview of the 8 Components of Lean: Value Stream Mapping, Workplace Organization, Predictability and Consistency, Set-up Reduction, TPM, Visual Factory, Support Processes, and Continuous Improvement.
Challenge
- An assessment of the learner’s progress in this course.

4.8 out of 5 stars
Comments from Learners About This Course
- Concise, accurate to industry best practices for Lean manufacturing.
- It helped me a lot to understand more about lean; thank you.
- Well detailed and well explained.
You may also be interested in…
- Lean Manufacturing – Online training that provides learners with a comprehensive understanding of how Lean Manufacturing works in a manufacturing environment.
- Lean for Business Processes – Online training that provides learners with a comprehensive understanding of how Lean Manufacturing works in a transaction-based/non-manufacturing business or job function.
- Lean for Job Shops – Online training in how to apply lean manufacturing techniques in short-run, job shop environments.