Resource Centers
Aerospace PPAP Packages
PPAPs in the Aerospace Industry are based on product and process data.
- The PPAP consists of the Documentation Package including the PPAP Approval Form and relevant part samples.
- To build the Documentation Package, use data on both the subject product or part and the corresponding process captured from a significant production run to complete the 11 Elements.
Elements of a Aerospace Industry PPAP Package
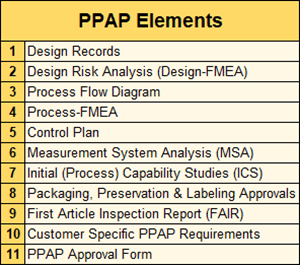
Element 1: Design Record
- The Design Record should include engineering specifications that define the product.
- Include full documentation of the Design Record in the PPAP File to ensure that both the supplier and customer are discussing and relying on the same component design and same product design revision level.
Element 2: Design Risk Analysis (Design-FMEA)
- A Design Risk Analysis involves the use of analytical techniques to identify potential risk (or failure modes) related to product performance, durability, manufacturability and cost.
- A Design-FMEA (DFMEA) is a well-known structured method for analyzing risk.
Element 3: Process Flow Diagrams
- A process flow diagram (or flowchart) shows the sequence of steps contained within a process in a visual or pictorial form.
- Types of flowcharts include Process Flowcharts, Functional (or Deployment) Flowcharts, Top-Down Flowcharts, SIPOC Diagrams and Value Stream Maps.
Element 4: Process-FMEA
- PFMEAs are used to identify potential process failures, the effects of a failure and the relative probability of that failure occurring.
- A PFMEA is a risk prioritization tool; the intent is to identify risks that are unacceptable and to initiate corrective plans that mitigate those risks.
Element 5: Control Plan
- Control Plans document the system to be used to monitor and control parts and processes.
- Control Plans identify process and product characteristics along with their specifications, sampling or testing intervals and test methods to monitor those characteristics.
- An important part of a Control Plan is well-thought-out reaction plans to be used in case an out-of-control condition occurs.
Element 6: Measurement System Analysis (MSA)
- The analysis of a measurement system involves understanding the uncertainties associated with taking a particular measurement and then, where possible, quantifying those uncertainties.
- The uncertainties that can be quantified (by statistical means) include issues of accuracy, linearity, stability, repeatability and reproducibility.
- A GR&R (Gage Repeatability & Reproducibility) study is used to determine if the measurement device or system can be relied upon or if the measurement system must be improved before it can be used.
Element 7: Initial (Process) Capability Studies (ICS)
- The purpose of Initial Capability Studies is to determine if production processes are stable and are potentially capable of meeting the specification.
Element 8: Packaging, Preservation and Labeling Approvals
- Detailed protocols for packaging of parts should include a picture of the packaging, displaying the related labeling.
- Labeling should include a way to identify the production order of the part by batch or lot number.
Element 9: First Article Inspection Report (FAIR)
- The purpose of the First Article Inspection is to give objective evidence that all engineering, design and specification requirements are correctly understood, accounted for, verified, and recorded.
- There are 3 FAIR forms:
- Form 1: Part Number Accountability
- Form 2: Product Accountability
- Form 3: Characteristic Accountability, Verification and Compatibility Evaluation
Element 10: Customer-Specific PPAP Requirements
- All requirements over and above the standard PPAP documentation level specified by the customer are included in this element.
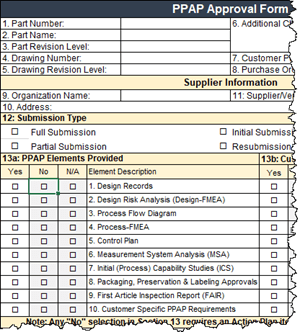
Element 11: PPAP Approval Form
- The PPAP Approval Form is a summary of the prior 10 Elements complete with supporting data.
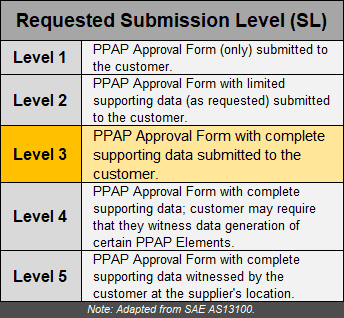
Levels of Submission
- There are 5 Levels of Submission for a PPAP Package; the levels have increasing higher levels of requirements for the supplier.
- Unless otherwise requested by the customer (or negotiated with the customer) the supplier should use submission requirements for the default level, Level 3.